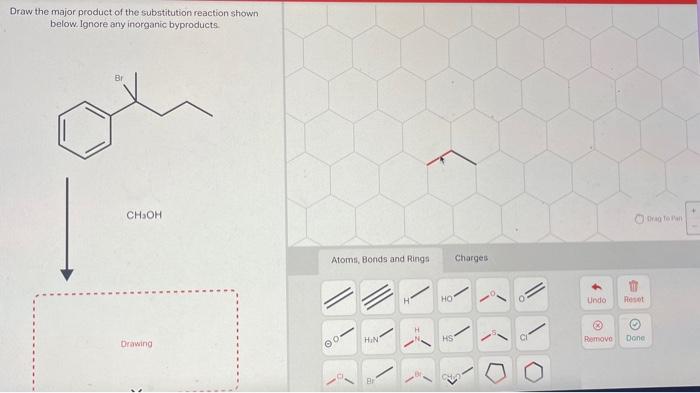
Draw the correct organic product for the oxidation reaction: – Oxidation reactions, a cornerstone of organic chemistry, offer a versatile tool for transforming organic molecules. In this in-depth guide, we delve into the intricacies of oxidation reactions, empowering you to accurately predict and synthesize the desired organic products.
This comprehensive exploration encompasses the fundamental concepts of oxidation reactions, unraveling the mechanisms that govern their regio- and stereoselectivity. With a focus on experimental considerations and practical applications, we equip you with the knowledge and skills to harness the power of oxidation reactions in various scientific endeavors.
Oxidation Reaction Definition
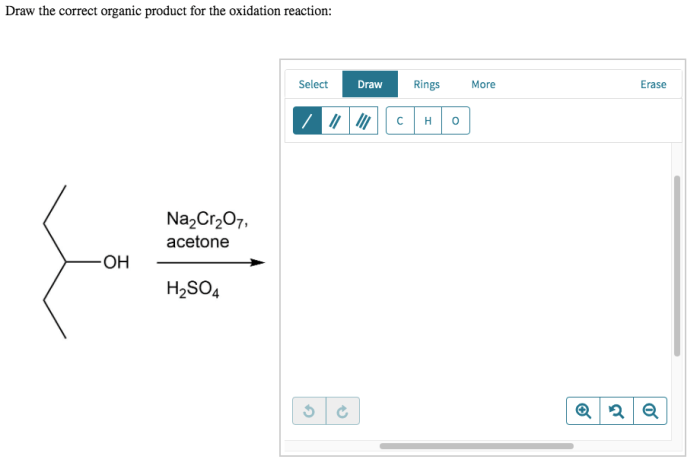
Oxidation reactions involve the loss of electrons by a molecule, atom, or ion. This process results in an increase in the oxidation state of the substance undergoing oxidation.
Common Oxidation Reactions
- Combustion: The reaction of a substance with oxygen, releasing energy in the form of heat and light.
- Rusting: The oxidation of iron in the presence of oxygen and moisture.
- Bleaching: The removal of color from a substance, typically using an oxidizing agent such as hydrogen peroxide or sodium hypochlorite.
Organic Product Identification
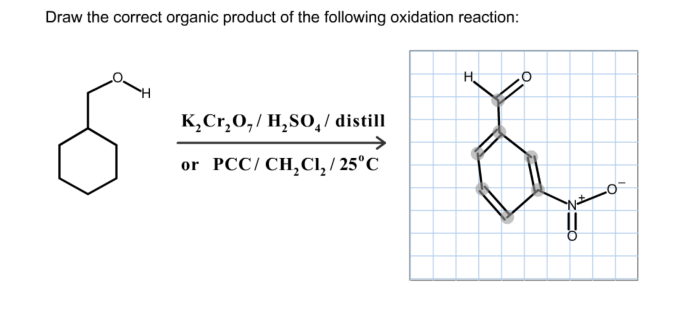
In oxidation reactions, the organic product is the compound formed when an organic molecule loses electrons.
Factors Influencing Organic Product Identity
- Nature of the oxidant
- Reaction conditions
- Substrate structure
Oxidation Mechanisms
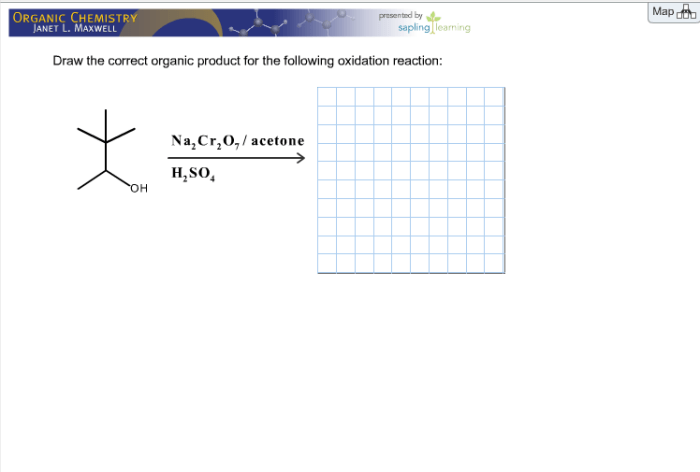
Oxidation reactions can proceed through various mechanisms, including:
Free Radical Oxidation
Involves the formation of free radicals, which are highly reactive species with unpaired electrons.
Electrophilic Addition
Involves the addition of an electrophile, a species that is attracted to electrons, to a double or triple bond.
Nucleophilic Substitution
Involves the substitution of a nucleophile, a species that donates electrons, for a leaving group.
Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity

Oxidation reactions can exhibit regioselectivity and stereoselectivity.
Regioselectivity
Refers to the preference for the reaction to occur at a specific site on the substrate.
Stereoselectivity
Refers to the preference for the reaction to produce a specific stereoisomer.
Experimental Considerations: Draw The Correct Organic Product For The Oxidation Reaction:
Safety Precautions
Oxidation reactions can be hazardous, so proper safety precautions must be taken.
Reaction Conditions, Draw the correct organic product for the oxidation reaction:
Reaction conditions, such as temperature, solvent, and catalyst, can affect the outcome of an oxidation reaction.
Purification Techniques
The organic product must be purified after the reaction to remove impurities.
Applications of Oxidation Reactions
Oxidation reactions have numerous applications in various fields, including:
Organic Synthesis
Used to prepare a wide range of organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and polymers.
Industrial Processes
Used in the production of chemicals, such as sulfuric acid and nitric acid.
Environmental Remediation
Used to treat pollutants, such as hydrocarbons and pesticides.
FAQ Guide
What is the fundamental concept behind oxidation reactions?
Oxidation reactions involve the loss of electrons from a molecule, leading to an increase in its oxidation state.
How can we predict the organic product of an oxidation reaction?
Factors such as the nature of the oxidizing agent, the substrate, and reaction conditions influence the identity of the organic product.
What is the significance of regio- and stereoselectivity in oxidation reactions?
Regio- and stereoselectivity dictate the specific location and orientation of functional groups in the organic product, enabling the synthesis of target molecules with precise structural features.