Embark on an enlightening journey with our comprehensive Hamlet study guide questions and answers PDF, a treasure trove of insights into Shakespeare’s timeless masterpiece. This guide unlocks the complexities of Hamlet’s character, unravels the play’s profound themes, and illuminates its enduring legacy.
Within these pages, you’ll delve into the intricacies of Hamlet’s psyche, exploring his motivations, relationships, and the profound impact they have on his actions. You’ll uncover the play’s central themes, tracing their evolution throughout the narrative and examining their significance in shaping the play’s overall meaning.
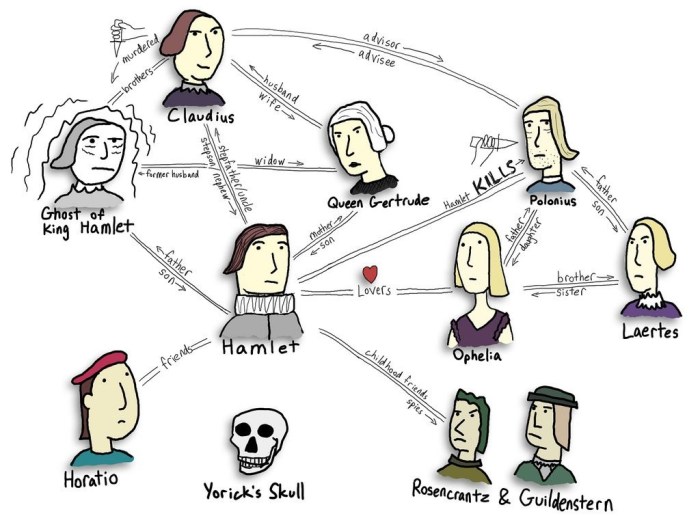
Character Analysis of Hamlet
Hamlet, the protagonist of Shakespeare’s eponymous tragedy, is a complex and enigmatic character. His introspective nature, moral dilemmas, and tragic flaw contribute to the play’s enduring appeal.
Hamlet’s Motivations
- Revenge: Hamlet is driven by a desire to avenge his father’s murder, but his indecisiveness and philosophical musings delay his actions.
- Grief: Hamlet’s grief over his father’s death and his mother’s hasty remarriage intensifies his melancholy and cynicism.
- Existential Questions: Hamlet grapples with fundamental questions about life, death, and the meaning of existence.
Hamlet’s Relationships
Hamlet’s relationships with other characters significantly impact his actions and decisions:
- Ophelia: Hamlet’s love for Ophelia is complicated by his grief, madness, and indecisiveness.
- Horatio: Horatio is Hamlet’s loyal friend and confidant, providing him with support and perspective.
- Claudius: Hamlet’s uncle and stepfather, who murdered his father, becomes the object of Hamlet’s revenge.
Themes and Motifs in Hamlet
Major Themes, Hamlet study guide questions and answers pdf
- Revenge: The play explores the moral implications and consequences of revenge, as well as the destructive nature of unchecked vengeance.
- Mortality: Hamlet’s existential musings and the deaths of several characters highlight the fragility and inevitability of human life.
- Madness: Hamlet’s feigned and actual madness becomes a symbol of the play’s themes of deception, chaos, and the instability of human reason.
Motifs
- The Ghost: The ghost of Hamlet’s father represents the supernatural, the unresolved past, and the weight of family obligations.
- The Play Within the Play: Hamlet uses the play to expose Claudius’s guilt and to confront his own moral dilemmas.
- Poison: The poison used in the play symbolizes corruption, deception, and the destructive power of secrets.
Plot Structure and Dramatic Devices
Structure
Hamlet follows a five-act structure, which builds suspense and tension through:
- Exposition: The first act introduces the characters and the conflict.
- Rising Action: The middle three acts develop the plot, reveal Claudius’s guilt, and Hamlet’s struggles.
- Climax: The climax in Act IV, Scene 5, when Hamlet finally confronts Claudius.
- Falling Action: The play concludes with a series of deaths and revelations.
- Resolution: The final scene resolves the conflict and provides a sense of closure.
Dramatic Devices
Shakespeare employs various dramatic devices to enhance the play’s impact:
- Foreshadowing: Hints and clues throughout the play foreshadow future events, creating a sense of anticipation.
- Irony: Dramatic irony occurs when the audience knows more than the characters, creating tension and suspense.
- Symbolism: The play uses symbols, such as the ghost and the play within the play, to convey deeper meanings and themes.
Literary and Historical Context of Hamlet
Historical Context
Hamlet was written during the Elizabethan era, a time of significant cultural and political changes.
- The Protestant Reformation: Hamlet’s religious doubts and existential musings reflect the religious turmoil of the time.
- The Rise of Humanism: The play’s focus on individual experience and reason aligns with the humanist ideals of the Renaissance.
- The Tudor Dynasty: The play’s themes of betrayal and succession resonate with the political struggles of the Tudor court.
Influence on the Play
The historical context influenced Hamlet’s characters, themes, and plot:
- Hamlet’s melancholy and introspective nature reflects the philosophical and religious debates of the time.
- The play’s themes of revenge and succession draw upon historical events, such as the assassination of Elizabeth I’s father.
- The play’s language and imagery reflect the cultural and intellectual climate of the Elizabethan era.
Modern Interpretations of Hamlet
Different Interpretations
Hamlet has been interpreted and adapted in numerous ways over the centuries, reflecting the changing cultural and social contexts.
- Romantic Era: Hamlet was seen as a tragic hero, emphasizing his sensitivity and introspective nature.
- Victorian Era: Hamlet was interpreted as a more complex and ambiguous character, with a focus on his psychological struggles.
- Modern Era: Hamlet has been interpreted as a symbol of alienation, existential angst, and the human condition.
Notable Adaptations
Some notable adaptations of Hamlet include:
- Laurence Olivier’s 1948 film adaptation, which emphasizes Hamlet’s psychological turmoil.
- Kenneth Branagh’s 1996 film adaptation, which is known for its opulent visuals and large cast.
- Michael Almereyda’s 2000 film adaptation, which sets the play in modern-day New York City.
Commonly Asked Questions: Hamlet Study Guide Questions And Answers Pdf
What is the significance of Hamlet’s soliloquies?
Hamlet’s soliloquies offer profound insights into his inner thoughts and emotions, revealing his struggles with morality, mortality, and the complexities of human nature.
How does the play’s setting contribute to its atmosphere and themes?
The castle of Elsinore, with its dark corridors and foreboding presence, creates a sense of isolation and unease, reflecting Hamlet’s own inner turmoil and the play’s exploration of themes such as death, betrayal, and madness.
What is the role of the ghost in the play?
The ghost of Hamlet’s father serves as a catalyst for the play’s events, revealing the truth about his murder and setting Hamlet on a path of revenge. It also raises questions about the nature of truth, justice, and the afterlife.