The Venn diagram for plants and animals is a valuable tool for understanding the unique characteristics and shared traits of these two kingdoms. By visually representing their similarities and differences, this diagram provides a comprehensive overview of the diversity of life on Earth.
This guide will explore the purpose and components of a Venn diagram for plants and animals, examining the defining features of each group and highlighting their key distinctions. Through this analysis, we will gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies and interconnectedness of the natural world.
Introduction: Venn Diagram For Plants And Animals
A Venn diagram is a graphical representation that illustrates the logical relationships between different sets. It is named after John Venn, a 19th-century British logician. Venn diagrams are used to visualize the similarities and differences between two or more sets.
They are particularly useful for comparing and contrasting concepts, ideas, or objects.
The purpose of a Venn diagram is to show the overlapping and non-overlapping areas between sets. This can help us to understand the relationships between the sets and to identify the elements that are common to all sets, as well as the elements that are unique to each set.
Objective
The objective of using a Venn diagram to compare plants and animals is to illustrate the similarities and differences between these two kingdoms of living organisms. By comparing the two sets, we can identify the characteristics that are common to both plants and animals, as well as the characteristics that are unique to each kingdom.
Plants and Animals
Define Plants
Plants are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that are characterized by their ability to photosynthesize, their possession of a cell wall, and their lack of motility.
Define Animals
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that are characterized by their ability to move, their possession of a nervous system, and their heterotrophic nutrition.
Characteristics of Plants
The characteristics of plants include:
- Multicellularity
- Eukaryotic cells
- Cell walls
- Chloroplasts
- Autotrophic nutrition
- Immobility
Characteristics of Animals, Venn diagram for plants and animals
The characteristics of animals include:
- Multicellularity
- Eukaryotic cells
- Lack of cell walls
- Heterotrophic nutrition
- Motility
- Nervous system
Venn Diagram for Plants and Animals
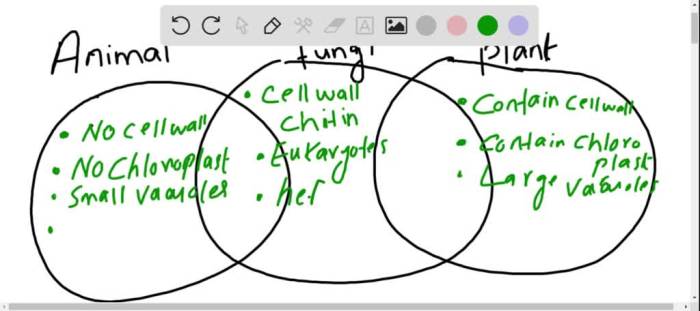
A Venn diagram is a graphical representation that shows the similarities and differences between two or more sets of data. In the case of plants and animals, a Venn diagram can be used to illustrate the characteristics that are unique to each group, as well as the characteristics that they share.
Similarities between Plants and Animals
Plants and animals are both living organisms, and they share a number of similarities. These similarities include:
- They are both made up of cells.
- They both require energy to survive.
- They both reproduce.
- They both respond to their environment.
Differences between Plants and Animals
While plants and animals share a number of similarities, they also have a number of differences. These differences include:
- Plants are autotrophs, meaning that they can produce their own food through photosynthesis. Animals are heterotrophs, meaning that they must consume other organisms to obtain energy.
- Plants have cell walls, while animals do not.
- Plants are typically stationary, while animals are mobile.
- Plants have a different reproductive system than animals.
Common Characteristics
The overlapping section of the Venn diagram represents the characteristics that are shared by both plants and animals. These characteristics include:
- They are both living organisms.
- They both require energy to survive.
- They both respond to their environment.
Similarities Between Plants and Animals
Plants and animals, despite their distinct characteristics, share fundamental similarities that highlight their shared evolutionary history and the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
One of the most significant similarities between plants and animals is their cellular structure. Both plants and animals are eukaryotic organisms, meaning their cells contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. This shared cellular architecture indicates a common ancestry and suggests that both groups evolved from a single-celled ancestor.
Cellular Processes
- Metabolism:Both plants and animals carry out metabolic processes to obtain energy and sustain life. Plants perform photosynthesis to convert sunlight into chemical energy, while animals obtain energy by consuming other organisms.
- Respiration:Plants and animals both undergo cellular respiration, a process that releases energy from organic molecules in the presence of oxygen.
- Reproduction:Plants and animals have evolved various reproductive strategies, including sexual and asexual reproduction. Many plants and animals produce specialized reproductive cells (gametes) that fuse to form a zygote, which develops into a new organism.
Growth and Development
Plants and animals exhibit similar patterns of growth and development. They both start as small, single-celled organisms that undergo cell division and differentiation to form multicellular structures.
- Growth:Plants grow by adding new cells to their existing tissues, while animals grow by increasing the size and number of their cells.
- Development:Plants and animals undergo a series of developmental stages, from embryonic development to maturity. These stages involve the formation of specialized tissues, organs, and organ systems.
Response to Stimuli
Plants and animals possess the ability to respond to various environmental stimuli, demonstrating their adaptability and sensitivity to their surroundings.
- Light:Plants respond to light through the process of phototropism, growing towards or away from light sources. Animals, such as insects, use light to navigate and find food.
- Temperature:Both plants and animals have evolved adaptations to withstand different temperature ranges, enabling them to survive in diverse habitats.
- Touch:Plants exhibit thigmotropism, responding to touch by growing towards or away from the point of contact. Animals use touch to interact with their environment and communicate with each other.
Differences Between Plants and Animals
Plants and animals exhibit fundamental differences in their characteristics, life processes, and modes of nutrition. These variations are crucial in understanding the distinct roles they play in ecosystems and the contrasting strategies they have evolved to survive.
One significant difference lies in their mode of nutrition. Plants are autotrophs, meaning they can synthesize their own food through photosynthesis. They possess chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll, a pigment that captures sunlight and converts it into chemical energy. In contrast, animals are heterotrophs, relying on consuming other organisms for nourishment.
They lack chloroplasts and must obtain energy from pre-existing organic matter.
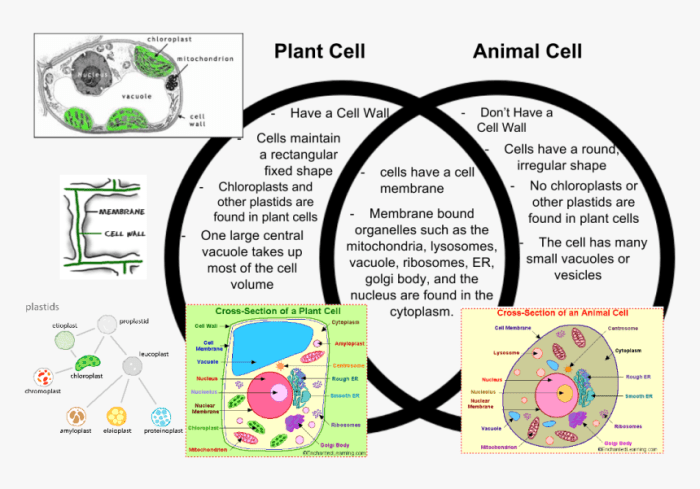
Cellular Structure
Another key difference is their cellular structure. Plant cells have a rigid cell wall composed of cellulose, which provides structural support and protection. They also possess a large central vacuole, which stores water and other substances. Animal cells, on the other hand, lack a cell wall and have a more flexible cell membrane.
They typically have smaller vacuoles and a more complex internal structure.
Reproduction
Reproduction is another area where plants and animals diverge. Plants can reproduce both sexually, through the production of seeds, and asexually, through vegetative propagation. Animals, on the other hand, typically reproduce sexually, although some species exhibit asexual reproduction methods such as budding or parthenogenesis.
Mobility
Mobility is a defining characteristic that distinguishes plants from animals. Plants are generally sessile, meaning they are rooted in one location and cannot move actively. Animals, on the other hand, are mobile and can move around to seek food, mates, or shelter.
Nervous and Sensory Systems
Plants lack a nervous system and sensory organs, relying on chemical and hormonal signals to respond to environmental stimuli. Animals, in contrast, have evolved complex nervous and sensory systems that enable them to detect and respond to a wide range of stimuli, including light, sound, and touch.
Significance of Differences
The differences between plants and animals have profound implications for their ecological roles and evolutionary histories. Plants provide the primary source of food for animals and serve as the foundation of food chains. Their ability to produce their own food through photosynthesis allows them to occupy a unique position in ecosystems.
Animals, on the other hand, play a crucial role in controlling plant populations, dispersing seeds, and facilitating nutrient cycling. Their mobility and sensory systems enable them to adapt to changing environments and exploit a wide range of resources.
Conclusion
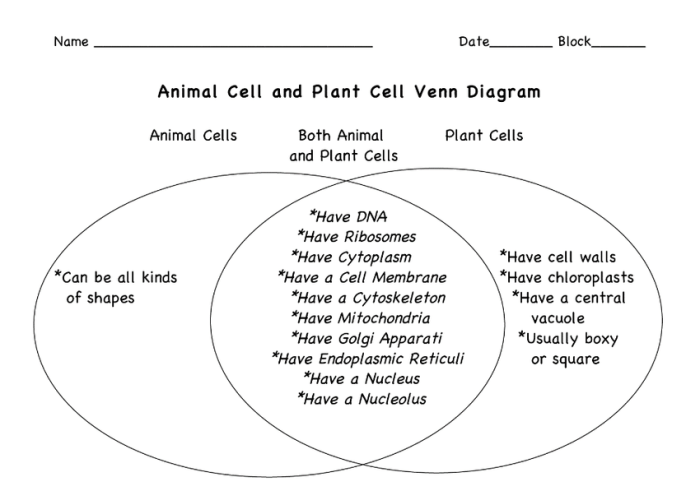
In conclusion, the Venn diagram provides a concise and effective method for comparing and contrasting two distinct groups. It visually represents the similarities and differences between plants and animals, making it easier to understand their unique characteristics and interrelationships.
The Venn diagram serves as a valuable tool for educators, researchers, and students alike, as it allows for quick and easy identification of key points. By identifying the overlapping and non-overlapping areas, it facilitates a deeper understanding of the two groups and their relationship to each other.
Applications of Venn Diagram
Beyond its use in biology, Venn diagrams have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Education:Venn diagrams are commonly used in educational settings to illustrate concepts and compare different topics or ideas.
- Business:Venn diagrams can be employed to compare different products, services, or market segments.
- Computer science:Venn diagrams are utilized to visualize relationships between different sets of data or objects.
- Psychology:Venn diagrams can be used to represent the overlapping and distinct characteristics of different psychological constructs.
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of a Venn diagram for plants and animals?
A Venn diagram for plants and animals is used to visually represent the similarities and differences between these two groups of organisms.
What are the defining characteristics of plants?
Plants are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that are autotrophic, meaning they can produce their own food through photosynthesis.
What are the defining characteristics of animals?
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophic, meaning they must consume other organisms to obtain energy.